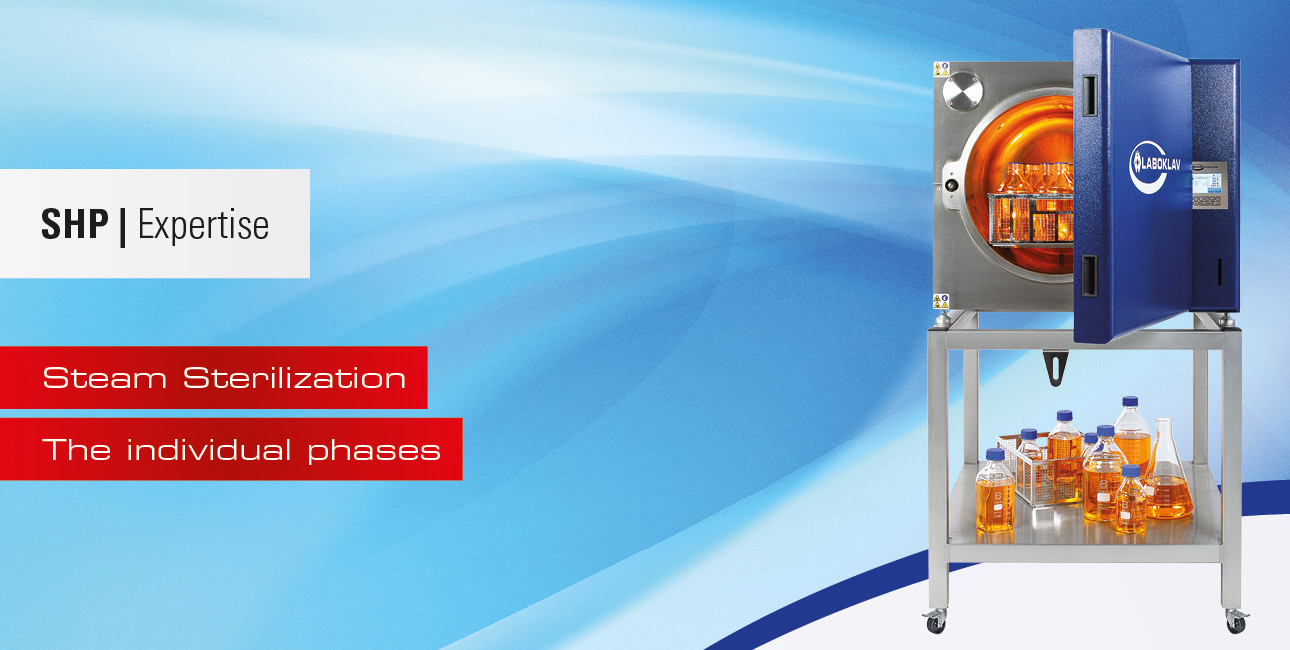
Sterilization process in the Autoclave: Heat-Up Time, Holding Time, and their Importance.
Phases of Steam Sterilization
An effective sterilization process in an autoclave is based on a precisely coordinated sequence of time intervals that ensures the complete elimination of microorganisms. In particular, the heat-up time and the holding time are crucial for the effectiveness of the sterilization.
1. Heat-Up Time – Heating and Evacuation
During the heat-up phase, both the chamber and the items to be sterilized are heated to the required temperature. Simultaneously, the chamber is vented or evacuated to create a saturated steam atmosphere.
This step is essential to ensure that steam reliably reaches all surfaces of the sterilization load.
2. Holding Time – The Actual Sterilization Phase
The holding time (formerly referred to as the "sterilization time") consists of two key components:
Equilibration Time:
This is the time span from the moment the sterilization temperature is reached at the chamber's reference measurement point until the temperature is reached throughout the entire load. Only once the entire load has reached the target temperature does the next phase begin.
Exposure Time:
The exposure time represents the actual duration of sterilizing action. During this phase, the temperature is kept constant within the specified sterilization range at all measurement points. Microorganisms are inactivated following two fundamental sterilization principles.
a. Lethality Time
This time span is experimentally determined and describes how long it takes to reliably kill a defined microorganism or spore under specific conditions.
b. Safety Margin
An additional calculated time period that provides a sufficient safety reserve – to compensate for any fluctuations or uncertainties in the load condition or process course.
Conclusion:
The correct execution of the heat-up and holding times is indispensable for the safety, reproducibility, and validation of the sterilization process. Only when these phases are strictly followed can a high microbial safety standard – especially in the medical field – be assured.
 DE
DE  EN
EN  PL
PL  FR
FR  ES
ES  SV
SV  NL
NL  AR
AR 

